What is Catalytic Converter?
A catalytic converter is an emissions control device that is installed in the exhaust system of internal combustion engines. It is designed to reduce the harmful pollutants in the exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere.
The main pollutants that catalytic converters target are carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). These pollutants are toxic and can cause serious health problems if they are inhaled, as well as being major contributors to air pollution.
Catalytic converters use a catalytic reaction to convert these pollutants into less harmful substances.
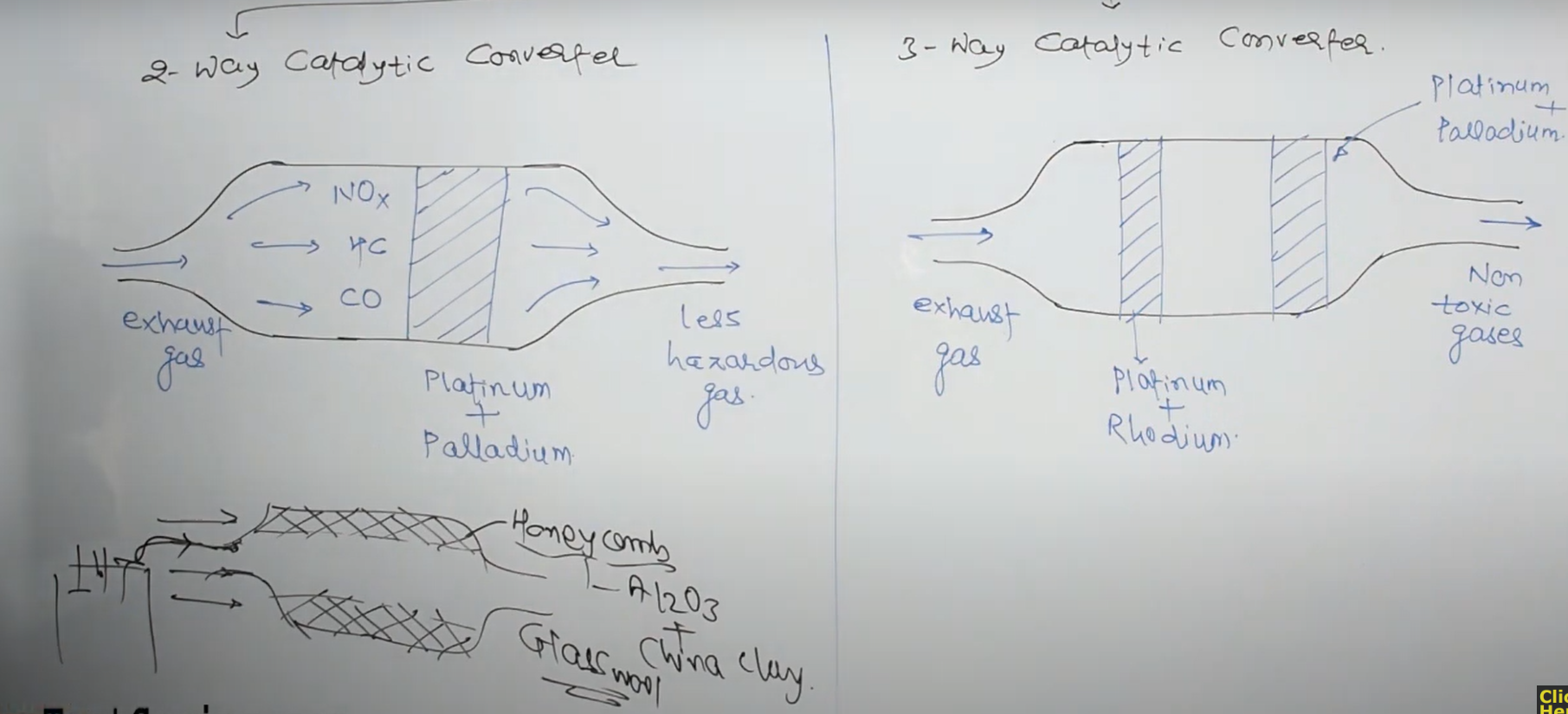 The converter contains a ceramic or metal substrate that is coated with a catalytic material, such as platinum, palladium, or rhodium.
The converter contains a ceramic or metal substrate that is coated with a catalytic material, such as platinum, palladium, or rhodium.
The catalytic material acts as a catalyst, which means that it speeds up the chemical reactions that take place inside the converter without being consumed in the process.
The exhaust gases from the engine enter the catalytic converter, where they pass through the catalytic material.
The high temperatures inside the converter cause the catalytic material to heat up and become active. As the exhaust gases pass through the converter, the catalytic material causes a chemical reaction to take place, which converts the pollutants into less harmful substances.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is converted into carbon dioxide (CO2), which is a harmless gas. Hydrocarbons (HC) are converted into water vapor (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are converted into nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2).
It is an extremely important component in the exhaust system of modern vehicles.
It helps to reduce the harmful emissions that are released into the atmosphere, which helps to improve air quality and protect public health. It have been mandatory for all vehicles sold in the United States since 1975 and in European Union since 1993.
Catalytic converters have several advantages over other emissions control devices, such as diesel particulate filters and selective catalytic reduction systems. They are relatively inexpensive, lightweight, and durable. They also require very little maintenance and can last the entire lifespan of a vehicle.
Types of Catalytic Converter?
There are several types, each designed to target specific pollutants in the exhaust gases:
- Oxidation catalytic converters: These converters use a platinum or palladium-based catalytic material that promotes an oxidation reaction, which converts carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrocarbons (HC) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). They are commonly used in gasoline engines.
- Three-way catalytic converters: These converters use a platinum, palladium and rhodium-based catalytic material that promotes oxidation, reduction and storage reactions. These converters can convert carbon monoxide (CO), hydrocarbons (HC) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) into carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O) and nitrogen (N2). They are commonly used in gasoline engines.
- Diesel oxidation catalytic converters: These converters use a catalytic material that promotes oxidation reactions to convert hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO) into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O). They are commonly used in diesel engines.
- Diesel particulate filters: These filters are used to remove particulate matter, also known as soot, from the exhaust gases of diesel engines. They use a ceramic or metallic substrate that captures the particulate matter, which can then be burned off at high temperatures.
- Selective catalytic reduction (SCR): This type of catalytic converter uses a urea-based solution to reduce the nitrogen oxides (NOx) in the exhaust gases of diesel engines into nitrogen and water vapor. The urea solution is injected into the exhaust stream, where it reacts with the NOx in the presence of a catalytic material, typically vanadium oxide, to break down the NOx into its harmless components.
The type is used in a vehicle or equipment depends on the engine type, emissions regulations and the specific pollutants to be targeted.
Who Invented This?
It was invented by a chemist and engineer named Eugene Houdry in the 1950s.
Houdry was born in France in 1898 and moved to the United States in the 1920s. He worked for several companies in the oil and gas industry before starting his own company, Oxy-Catalyst Corporation, in the 1950s.
Houdry became concerned about the high levels of air pollution in Southern California caused by the oil refineries in the area.
He began researching ways to reduce the emissions from these refineries and discovered that a catalytic converter could be used to remove harmful pollutants from the exhaust gases.
Houdry developed the first catalytic converter, which used a ceramic substrate coated with platinum and palladium as the catalytic material.
He also developed a process for mass-producing the converters, which made them more affordable and accessible to the public.
Houdry’s invention was first used in automobiles in 1975, and catalytic converters have been mandatory for all vehicles sold in the United States since that time.
Today, catalytic converters are used in vehicles, power plants and other industrial sources around the world to reduce emissions and improve air quality.
Houdry received several awards and honors for his work, including the National Medal of Technology and the National Environmental Protection Act (NEPA) award.
Frequently Asked Questions-
can It Damage Engine?
A catalytic converter can malfunction or fail, but it is unlikely for it to cause damage to the engine. However, certain conditions or issues can lead to problems with the catalytic converter that may damage the engine or cause other issues.
A clogged catalytic converter can cause a restriction in the exhaust system, which can lead to decreased engine performance and increased engine temperature. This can cause damage to the engine if not addressed.
A catalytic converter can also become clogged if there is an issue with the engine, such as a misfire or oil consumption, that causes excess fuel or oil to enter the exhaust system.
A damaged catalytic converter can also cause the engine to run too lean or too rich, which can lead to poor performance, increased emissions, and damage to the engine.
A catalytic converter can also become damaged if it is exposed to high temperatures, such as in the case of a vehicle fire, which can cause the catalytic material to break down or become deformed.
If the catalytic converter has failed or malfunctioning, it’s important to address the issue as soon as possible. Failure to do so can cause the vehicle to fail emissions tests and potentially cause damage to the engine.
In summary, a properly working catalytic converter will not destroy the engine, but if it’s malfunctioning it can cause problems that lead to engine damage if not addressed.
Does it reduce fuel consumption?
A properly functioning catalytic converter will not significantly reduce fuel consumption on its own. However, in some cases, a malfunctioning catalytic converter can cause increased fuel consumption.
A clogged catalytic converter can cause a restriction in the exhaust system, which can lead to decreased engine performance and increased engine temperature. This can cause the engine to work harder and use more fuel to produce the same amount of power.
Also, if the catalytic converter is not working properly, it may not be able to efficiently convert pollutants in the exhaust gases, which can cause the engine to run too rich or too lean. This can lead to increased emissions and decreased fuel efficiency.
On the other hand, some advanced catalytic converters, such as lean NOx catalysts, can help reduce fuel consumption by reducing the nitrogen oxides emissions which can help the engine to run more efficiently, but this is not the main function of the catalytic converter.
In summary, a properly working catalytic converter will not significantly reduce fuel consumption, but a malfunctioning catalytic converter can cause increased fuel consumption.
Keep Reading- What is Carburetor and Types of Carburetor
What happens to car if we removed it?
Removing a catalytic converter from a vehicle can have several consequences:
- Increased emissions: The catalytic converter is an emissions control device that helps reduce the pollutants in the exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere. Without a catalytic converter, the emissions from the vehicle will be significantly higher, which can contribute to air pollution and have negative effects on public health.
- Reduced engine performance: A catalytic converter can also act as a restriction in the exhaust system. When it’s removed, the exhaust gases can flow more freely, which can improve the engine’s performance, but this increase in performance is usually minimal.
- Legal issues: In most countries, catalytic converters are mandatory for all vehicles and it’s illegal to remove them. If a vehicle is found to be operating without a catalytic converter, the owner can face fines and penalties.
- Decreased fuel efficiency: Without this device, the engine may run too rich, consuming more fuel and producing more emissions.
- Increased engine wear and tear: Without this device, the engine will produce more pollutants, which can cause damage to the engine components and lead to increased wear and tear over time.
In summary, removing this device can cause increased emissions, reduced engine performance, legal issues, decreased fuel efficiency, and increased engine wear and tear. It’s important to keep the device in good working condition to ensure that the engine is running efficiently and to comply with emissions regulations.
Keep Reading- Rating of SI and CI Engine Fuels
How much does a catalytic converter cost?
The cost this can vary depending on several factors such as the make, model and year of the vehicle, the type of catalytic converter, and where it’s purchased.
On average, it price for a passenger vehicle can cost anywhere from $100 to $2,000 or more, with the most common catalytic converters costing between $200 and $1,000.
High-performance vehicles or luxury cars can cost more than $2,000. The cost of the catalytic converter may also vary depending on the material it’s made of.
If the device has to be replaced due to a malfunction, it would typically be covered under the vehicle’s emissions warranty, if it still applies. If the catalytic converter needs to be replaced due to age or wear and tear, the cost will typically be the responsibility of the vehicle owner.
It’s important to note that it’s illegal in most countries to remove or tamper with a catalytic converter and the fines for doing so can be substantial.
In addition, a vehicle that does not have a properly functioning catalytic converter may not pass emissions testing and may not be able to be registered or operated on public roads.
In summary, the cost this device can vary widely, but on average, it can cost anywhere from $100 to $2,000 or more, depending on the vehicle and the type of catalytic converter.
It’s important to consider the cost of the replacement in relation to the potential fines, penalties or legal issues that may arise if the catalytic converter is removed.
Keep Reading- What is reversed Carnot cycle
What causes catalytic converter to fail?
There are several factors that can cause a catalytic converter to fail:
- Overheating: It needs to be at a certain temperature in order to function properly. If the converter gets too hot, the catalytic material can break down or become deformed, which can cause it to lose its effectiveness. Overheating can be caused by a malfunctioning engine, such as a misfire, which can cause excess fuel to enter the converter and cause it to overheat.
- Clogging: It can become clogged if there is an issue with the engine, such as a misfire or oil consumption, that causes excess fuel or oil to enter the exhaust system. A clogged converter can cause a restriction in the exhaust system, which can lead to decreased engine performance and increased engine temperature.
- Age: Over time, the catalytic material in the converter can become less effective as it becomes coated with carbon and other materials. This can cause the converter to lose its ability to reduce emissions.
- Exposure to contaminants: Exposure to contaminants such as sulfur and lead can also cause damage to this device, making it less effective.
- Physical damage: Physical damage to it, such as from an accident or exposure to high temperatures can cause the converter to malfunction or fail.
In summary, it can fail due to overheating, clogging, age, exposure to contaminants and physical damage.
Proper maintenance of the vehicle and regular check-ups can help to prolong the life of this device and avoid costly replacements.